Breast Augmentation
What is Breast Augmentation?
Breast augmentation surgery involves using implants to increase the size of your breasts or restore breast volume that has been lost after weight reduction or pregnancy. Breast augmentation can:
- Increase fullness and projection of your breasts.
- Improve the balance of your figure.
- Enhance your self-image and self-confidence.
Breast augmentation is a very personal procedure and you should do it for yourself, not for someone else. Breast augmentation is a good option if:
- You are physically healthy
- You have realistic expectations
- Your breasts are fully developed
- You are bothered by the feeling that your breasts are too small
- You are dissatisfied with your breasts losing shape and volume after pregnancy, weight loss, or with aging
- You are unhappy with the upper part of your breast appearing "empty"
- Your breasts are asymmetrical
- One or both breasts failed to develop normally or have an elongated shape
What it won't do
Breast augmentation does not correct severely drooping breasts. If you want your breasts to look fuller and to be lifted due to sagging, a breast lift may be required in conjunction with breast augmentation.
Breast lifting can often be done at the same time as your augmentation or may require a separate operation. Your plastic surgeon will assist you in making this decision.
Consultation and Preparing for Surgery
During your consultation be prepared to discuss:
- Why you want the surgery, your expectations, and the desired outcome
- Medical conditions, drug allergies, and previous medical treatments
- Current medications, vitamins, herbal supplements, alcohol, tobacco, and drug use
- Family history of breast cancer and results of any mammograms or previous biopsies
Your plastic surgeon will also:
- Evaluate your general health status and any pre-existing health conditions or risk factors
- Examine and measure your breasts, including detailed measurements of their size and shape, skin quality, and placement of your nipples and areolas
- Take photographs
- Discuss your options and recommend a course of treatment
- Discuss likely outcomes of breast augmentation and any risks or potential complications
Prior to surgery, you may be asked to:
- Get a blood test
- Take certain medications or adjust your current medications
- Stop smoking
- Avoid taking aspirin and certain anti-inflammatory drugs as they can increase bleeding
Breast augmentation surgery may be performed in an accredited outpatient or ambulatory surgical center or a hospital.
Be sure to ask your plastic surgeon questions. It's very important to understand all aspects of your breast augmentation surgery. It's natural to feel some anxiety, whether it's excitement for your anticipated new look or a bit of preoperative stress. Don't be shy about discussing these feelings with your plastic surgeon.
Augmentation Options
Implant choices
Saline implants are filled with sterile salt water. Should the implant shell leak, a saline implant will collapse and the saline will be absorbed and naturally expelled by the body. They provide a uniform shape, firmness and feel. Saline implants are FDA-approved for augmentation in women age 18 or older.
Silicone implants are filled with silicone gel. The gel feels a bit more like natural breast tissue. If the implant leaks, the gel may remain within the implant shell, or may escape into the breast implant pocket. A leaking implant filled with silicone gel will not collapse. If you choose these implants, you may need to visit your plastic surgeon regularly to make sure the implants are functioning properly. An ultrasound or MRI screening can assess the condition of breast implants. Silicone implants are FDA-approved for augmentation in women age 22 or older.
Form-stable implants are sometimes referred to as gummy bear implants because they maintain their shape even when the implant shell is broken. The consistency of the silicone gel inside the implant is thicker than traditional silicone gel implants. These implants are also firmer than traditional implants, but are thought to be less likely to break.
Form-stable implants are shaped rather than round. They have more projection at the bottom and are tapered towards the top. If a shaped implant rotates, it may lead to an unusual appearance of the breast. Placement of form-stable implant requires a longer incision in the skin.
Round implants have a tendency to make breasts appear fuller than form-stable implants. Higher profile options can achieve even more projection. Because round implants are the same shape all over, there is less concern about them rotating out of place.
Surface Texture
Smooth breast implants are the softest feeling. These implants can move with the breast implant pocket, which may give more natural movement. These implants may have some palpable or visible rippling.
Textured breast implants develop scar tissue to stick to the implant, making them less likely to move around inside of the breast and get repositioned. Texturing offers some advantage in diminishing the risk of a tight scar capsule.
Other options
Fat grafting A fat transfer breast augmentation essentially uses liposuction to take fat from other parts of your body and inject it into your breasts. This is an option for women who are looking for a relatively small increase in breast size and would prefer natural results. Risks include cysts, infection, microcalcification, necrosis (death) of fat cells and the possibility that some of the transferred fat cells will leave the breast area. Your plastic surgeon may also have you use a tissue expansion system during the weeks before your surgery to improve your results. You may have to have touch-up injections to retain your improved shape if you choose this surgery.
Your plastic surgeon will take into account your wishes and concerns and will choose the right breast augmentation option for you.
Implant manufacturers occasionally introduce new styles and types of implants, so there may be additional options available. Whether you choose saline or silicone implants, it is important for you to monitor your breast implants and follow-up with your plastic surgeon for appropriate checkups.
The Procedure
Step 1 - Anesthesia
Medications are administered for your comfort during the surgical procedure. The choices include intravenous sedation and general anesthesia. Your doctor will recommend the best choice for you.
Step 2 - The incision
Incisions are made in inconspicuous areas to minimize visible scarring. You and your plastic surgeon will discuss which incision options are appropriate for your desired outcome. Incision options include:
Periareolar incision
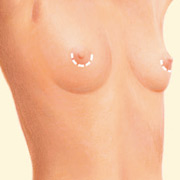
Inframammary incision
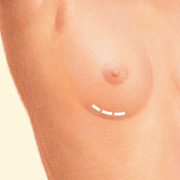
Transaxillary incision
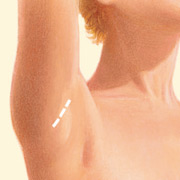
Incisions vary based on the type of implant, degree of enlargement desired, your particular anatomy, and patient-surgeon preference.
Step 3 - Inserting and placing the implant
After the incision is made, a breast implant is inserted into a pocket either:
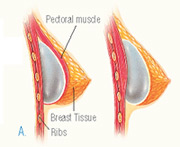
A. Under the pectoral muscle (a submuscular placement), or
B. Directly behind the breast tissue, over the pectoral muscle (a submammary/subglandular placement)
The method for inserting and positioning implants depends on the type of implant, degree of enlargement desired, your body type, and your surgeon's recommendations.
Step 4 - Closing the incisions
Incisions are closed with layered sutures in the breast tissue and with sutures, skin adhesive or surgical tape to close the skin.
Over time the incision lines will fade.

Step 5 - See the results
The results of breast augmentation are immediately visible. Over time, post-surgical swelling will resolve and incision lines will fade. Satisfaction with your new image should continue to grow as you recover and realize the fulfillment of your goal for fuller breasts.
Risks and Safety
The decision to have breast augmentation surgery is extremely personal and you'll have to decide if the benefits will achieve your goals and if the risks and potential complications are acceptable. Your plastic surgeon and/or staff will explain in detail the risks associated with surgery. You will be asked to sign consent forms to ensure that you fully understand the procedure and any risks and potential complications.
Possible risks include:
- Anesthesia risks
- Bleeding
- Infection
- Changes in nipple or breast sensation
- Poor scarring of skin
- Wrong or faulty position of the implant
- Implant leakage or rupture
- The formation of tight scar tissue around the implant (capsular contracture)
- Fluid accumulation (seroma)
- Wrinkling of the skin over the implant
- Pain, which may persist
- Possibility of revisional surgery
- The development of a type of cancer of the immune system called Breast Implant- Associated Anaplastic Large Cell Lymphoma (BIA-ALCL)
- Breast implants may be associated with systemic symptoms commonly referred to as breast implant illness (BII) which can include fatigue, "brain fog," muscle or joint pain and rash.
These risks and others will be fully discussed prior to your consent. It is important that you address all your questions directly with your plastic surgeon.
Other important considerations:
- Breast implants are not guaranteed to last a lifetime and future surgery may be required to replace one or both implants
- Pregnancy, weight loss and menopause may influence the appearance of augmented breasts over the course of your lifetime
- Breast augmentation requires regular examinations of your breasts' health and to evaluate the condition of your implants
Recovery After Surgery
After surgery you will be taken into a recovery area to be closely monitored. Your breasts will be wrapped in gauze dressings and an elastic bandage or support bra will minimize swelling and support the breasts as they heal. You may be permitted to go home after a few hours.
Before leaving, you will be given specific instructions that may include how to care for your breasts following surgery, medications to apply or take orally to aid healing and reduce the risk of infection, and when to follow-up with your plastic surgeon. You may be instructed to wear a support bra around the clock for the first week or two. It will be important to cleanse the incision sites and apply ointment as directed. Be sure to follow all instructions carefully.
After a post-surgical recovery period of 24 to 48 hours and an additional reduced-activity period of a few days, you will likely experience soreness and swelling for a few weeks. Exercise and normal activity can resume at the direction of your plastic surgeon.
Results
The results of breast augmentation are immediately visible. Over time, post-surgical swelling will subside and incision lines will fade. Satisfaction with your new image should continue to grow as you fully recover from surgery. In order to achieve optimal results, it is important that you follow your surgeon's post-operative instructions and return for follow-up visits.
It's important to know that breast implants are not designed to last a lifetime. Your implants may need to be replaced. You should plan for an annual examination by your plastic surgeon to evaluate your breast health and implant integrity.
Over time, your breasts can change due to aging, weight fluctuations, hormonal factors and gravity. If, after a period of years, you become dissatisfied with the appearance of your breasts, you may choose to undergo a breast lift or implant exchange to restore a more youthful contour.
Cost
Prices for breast augmentation can vary. The cost of the surgery may be based on the surgeon's experience, the type of breast implant used, and geographic office location. Many plastic surgeons offer patient financing plans, so be sure to ask.
Cost may include:
- Anesthesia fees
- Hospital or surgical facility costs
- Medical tests
- Post-surgery garments
- Prescriptions for medication
- Surgeon's fee
Most health insurance does not cover cosmetic surgery or its complications.
Your satisfaction involves more than a fee:
When choosing a plastic surgeon for a breast augmentation, remember that the surgeon's experience and your comfort with him or her is just as important as the final cost of the surgery. Plastic surgery involves many choices. The first and most important is selecting a member of the American Society of Plastic Surgeons (ASPS) you can trust. ASPS member surgeons meet rigorous standards:
- Board certification by the American Board of Plastic Surgery® (ABPS) or in Canada by The Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada®
- Complete at least six years of surgical training following medical school with a minimum of three years of plastic surgery residency training
- Pass comprehensive oral and written exams
- Graduate from an accredited medical school
- Complete continuing medical education, including patient safety each year
- Perform surgery in accredited, state-licensed, or Medicare-certified surgical facilities
Do not be confused by other official sounding boards and certifications.
The ABPS is recognized by the American Board of Medical Specialties (ABMS), which has approved medical specialty boards since 1934. There is no ABMS recognized certifying board with "cosmetic surgery" in its name. By choosing a member of The American Society of Plastic Surgeons, you can be assured that you are choosing a qualified, highly trained plastic surgeon who is board-certified by the ABPS or The Royal College of Physicians and Surgeons of Canada.
This procedural information is intended strictly for educational purposes. Only models are depicted in these procedural information pages. It is not intended to make any representations or warranties about the outcome of any procedure. It is not a substitute for a thorough, in-person consultation with a board certified plastic surgeon.
